<a href="http://www.shutterstock.com/pic-94126963/stock-photo-a-dead-honey-bee-showing-many-details-of-body-legs-and-mouth-parts-apis-mellifera.html?src=LmKgj8V1VCv2S_dCMh_s7A-1-1">Armando Frazao</a>/Shutterstock
Bees are dying in record numbers—and now the government admits that an extremely common pesticide is at least partially to blame.
For more than a decade, the Environmental Protection Agency has been under pressure from environmentalists and beekeepers to reconsider its approval of a class of insecticides called neonicotinoids, based on a mounting body of research suggesting they harm bees and other pollinators at tiny doses. In a report released Wednesday, the EPA basically conceded the case.
Marketed by European chemical giants Syngenta and Bayer, neonics are the most widely used insecticides both in the United States and globally. In 2009, the agency commenced a long, slow process of reassessing them—not as a class, but rather one by one (there are five altogether). Meanwhile, tens of millions of acres of farmland are treated with neonics each year, and the health of US honeybee hives continues to be dismal.
The EPA’s long-awaited assessment focused on how one of the most prominent neonics—Bayer’s imidacloprid—affects bees. The report card was so dire that the EPA “could potentially take action” to “restrict or limit the use” of the chemical by the end of this year, an agency spokesperson wrote in an emailed statement.
Reviewing dozens of studies from independent and industry-funded researchers, the EPA’s risk-assessment team established that when bees encounter imidacloprid at levels above 25 parts per billion—a common level for neonics in farm fields—they suffer harm. “These effects include decreases in pollinators as well as less honey produced,” the EPA’s press release states.
The crops most likely to expose honeybees to harmful levels of imidacloprid are cotton and citrus, while “corn and leafy vegetables either do not produce nectar or have residues below the EPA identified level.” Note in the below USGS chart that a substantial amount of imidacloprid goes into the US cotton crop.
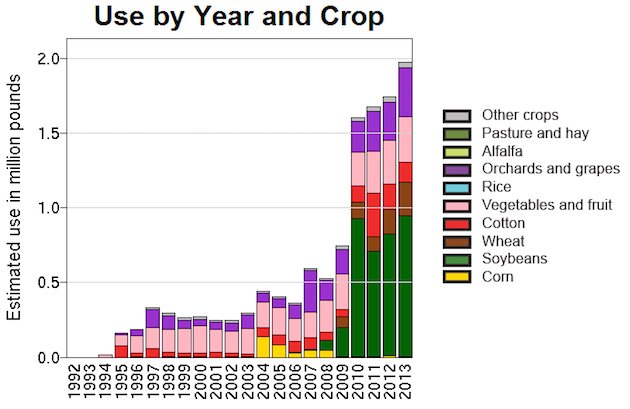
Meanwhile, the fact that the EPA says imidacloprid-treated corn likely doesn’t harm bees sounds comforting, but as the same USGS chart shows, corn gets little or no imidacloprid. (It gets huge amounts of another neonic, clothianidin, whose EPA risk assessment hasn’t been released yet.)
The biggest imidacloprid-treated crop of all is soybeans, and soy remains an information black hole. The EPA assessment notes that soybeans are “attractive to bees via pollen and nectar,” meaning they could expose bees to dangerous levels of imidacloprid, but data on how much of the pesticide shows up in soybeans’ pollen and nectar are “unavailable,” both from Bayer and from independent researchers. Oops. Mind you, imidacloprid has been registered for use by the EPA since the 1990s.
The agency still has to consider public comments on the bee assessment it just released, and it also has to complete a risk assessment of imidacloprid’s effect on other species. In addition to their impact on bees, neonic pesticides may also harm birds, butterflies, and water-borne invertebrates, recent studies suggest. Then there are the assessments of the other four neonic products that need to be done. Meanwhile, a coalition of beekeepers and environmental groups filed a lawsuit in federal court Wednesday pointing out that the agency has never properly assessed neonics in their most widely used form: as seed coatings, which are then taken up by crops.