PricewaterhouseCoopers, also known as PWC. Kristoffer Tripplaar/Sipa USA/AP
With every year that passes, we’re getting further away from averting a human-caused climate disaster. That’s the key message in this year’s “Low Carbon Economy Index,” a report released by the accounting giant PricewaterhouseCoopers.
The report highlights an “unmistakable trend”: The world’s major economies are increasingly failing to do what’s needed to to limit global warming to 3.6 degrees Fahrenheit above preindustrial levels. That was the target agreed to by countries attending the United Nations’ 2009 climate summit; it represents an effort to avoid some of the most disastrous consequences of runaway warming, including food security threats, coastal inundation, extreme weather events, ecosystem shifts, and widespread species extinction.
To curtail climate change, individual countries have made a variety of pledges to reduce their share of emissions, but taken together, those promises simply aren’t enough. According to the PricewaterhouseCoopers report, “the gap between what we are doing and what we need to do has again grown, for the sixth year running.” The report adds that at current rates, we’re headed towards 7.2 degrees Fahrenheit of warming by the end of the century—twice the agreed upon rate. Here’s a breakdown of the paper’s major findings.
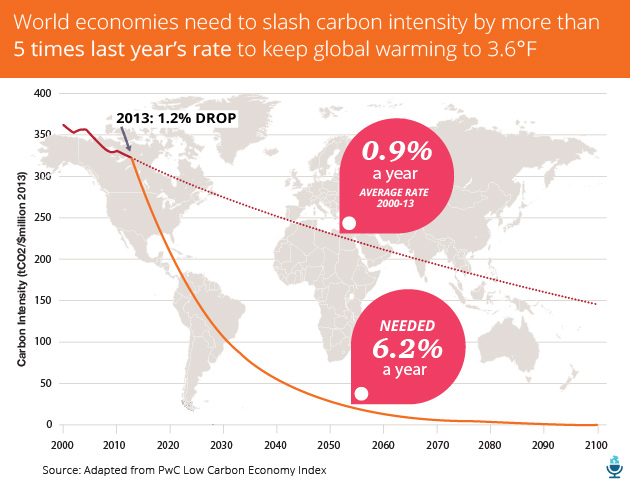
The chart above compares our current efforts to cut “carbon intensity”—measured by calculating the amount of carbon dioxide emitted per million dollars of economic activity—with what’s actually needed to rein in climate change. According to the report, the global economy needs to “decarbonize” by 6.2 percent every year until the end of the century to limit warming to 3.6 degrees Fahrenheit. But carbon intensity fell by only 1.2 percent in 2013.
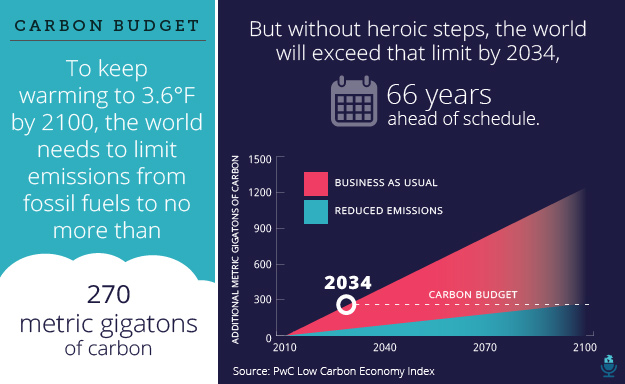
The report also found that the world is going to blow a hole in its carbon budget—the amount we can burn to keep the world from overheating beyond 3.6 degrees:
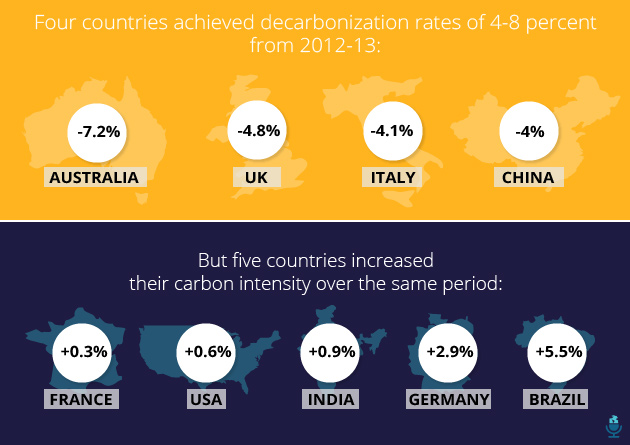
The report singles out countries that have done better than others when it comes to cutting carbon intensity. Australia, for example, tops the list of countries that have reduced the amount of carbon dioxide emitted per unit of GDP, mainly due to lower energy demands in a growing economy. But huge countries like the United States, Germany, and India are still adding carbon intensity, year-on-year:
Overall, PricewaterhouseCoopers paints a bleak picture of a world that’s rapidly running out of time; the required effort to curb global emissions will continue to grow each year. “The timeline is also unforgiving. The [Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change] and others have estimated that global emissions will need to peak around 2020 to meet a 2°C [3.6 degrees F] budget,” the report says. “This means that emissions from the developed economies need to be consistently falling, and emissions from major developing countries will also have to start declining from 2020 onwards.” G20 nations, for example, will need to cut their annual energy-related emissions by one-third by 2030, and by just over half by 2050. The pressure will be on the world’s governments to come up with a solution to this enormous challenge at the much-anticipated climate talks in Paris next year.