Little brown bats hibernate in a cave in Tennessee. Amy Smotherman Burgess/ZUMAPRESS
Silhouetted against an orange harvest moon, fluttering out of a haunted house, or circling Count Dracula’s cape: We often think of bats as creepy, especially this time of year.
But actually, these maligned creatures are crucial to many ecosystems—and our economy. What’s more, they’re in trouble. A few important facts to know about our winged, insect-munching friends:

Bats save us billions of dollars a year. Bats eat their bodyweight in insects every night. In 2011, researchers at the University of Tennessee, Knoxville used modeling techniques to calculate how much bats’ amazing insect-eating abilities are worth to US farmers. The estimates included the value of prevented crop damage from pests that bats eat, as well as the amount of money farmers would have to spend on pesticides to do the same job. They came up with a wide—but staggering—range: between $3 billion and $53 billion dollars a year.
A few years later, Josiah Maine, then a graduate student at Southern Illinois University’s Cooperative Wildlife Research lab, decided to test out those estimates on the most important American crop: corn. Maine’s team set up enclosures around corn fields that let in insects but prevented bats from entering and foraging, and then measured how that corn fared compared with corn in fields where bats could eat insects to their hearts’ desire—and found 50 percent more fungal growth and crop damage in the enclosed corn. They then estimated the cost of damage per acre and extrapolated it across all the acres of corn grown in the world. The total price tag? More than $1 billion per year, not including the cost of downstream environmental damage caused by increased pesticide use.

Bats prevent disease. A common misconception is that most bats carry rabies and other diseases. In fact, the vast majority of bats don’t have rabies, and out of more than 1,300 species of bats, only three suck the blood of other animals (and only one of other mammals). On the other hand, bats eat insects that spread diseases we really should be worried about. According to David Blehert, who leads the US Geological Survey’s Wildlife Disease Diagnostics Lab, bats play an important role controlling the spread of West Nile virus.
Without bats, there would be no tequila. Many species of bats pollinate plants. After they use their insanely long tongues to feast on the sweet nectar of flowers, pollen collects on their muzzles, which they spread from the male part of the flower to the female part of the flower.
More than 300 species of plants depend on bats to survive in many tropical and desert ecosystems. These include plants that humans eat, like the agave used to make tequila, as well as banana, peach, and mango trees.
Bats help save forests. Fruit-eating bats also play a crucial role in rejuvenating clear-cut rainforests. After a rainforest ecosystem is decimated, the first step toward rebuilding is the spreading of seeds by the poop of fruit-eating birds, bats, and other animals. But bats, which cover large distances to forage for fruit at night, do the best job at spreading “pioneer” plants, the flora that first begin to grow after clear cutting.
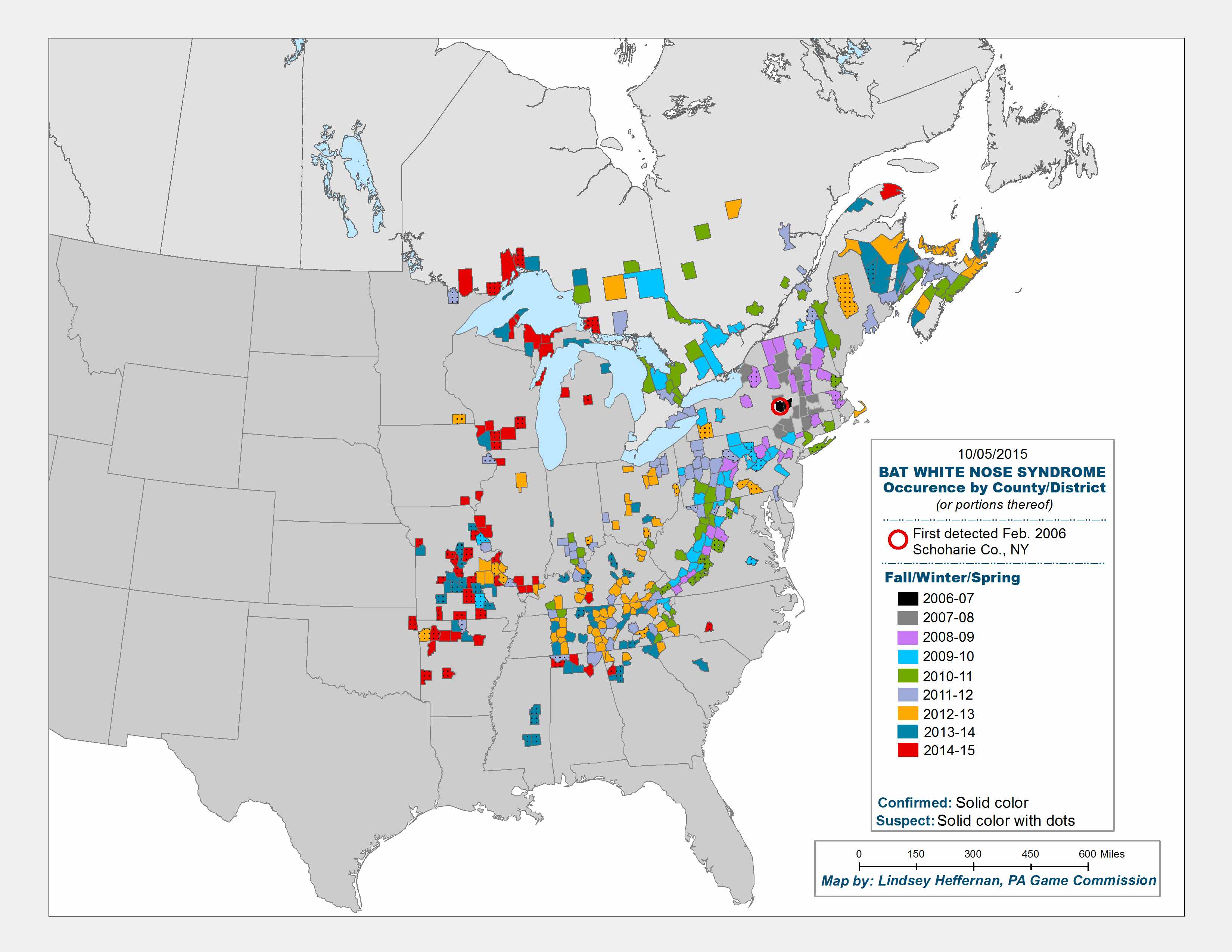
In North America, bats are in big trouble. Bats are dying in unprecedented numbers in the eastern United States and Canada, thanks to a terrifying fungal disease. Nearly 6 millions bats have perished in the past decade, including more than 90 percent of the populations of some species.
The recent bat troubles began about a decade ago, when a nasty fungus called Pseudogymnoascus destructans (Pd) found its way into caves full of hibernating bats in upstate New York. Unlike bacteria and other pathogens, this fungus thrives in cold temperatures and finds an ideal host in the sleeping bats. It creeps onto their muzzles and spreads on the skin covering their wings, irritating them and causing them to wake and move before they are supposed to. This disrupts their energy conservation and fat storage, causing bats to die before hibernation is over or leave their caves too early and starve outside.
Perhaps most frightening of all, the disease has spread very quickly: Since 2006 when wildlife biologists first identified it in New York, it has appeared in 26 states and five Canadian provinces. (Although in some of those states the effects have yet to be seen; bats don’t start dying until a year or more after the fungus arrives in their caves.) Within the next decade or so, white-nose syndrome is expected to reach states as far west as Wyoming.* White-nose syndrome has affected half of the 47 bat species in the United States, including the once ubiquitous little brown bat and the northern long-eared bat, which is now a threatened species.
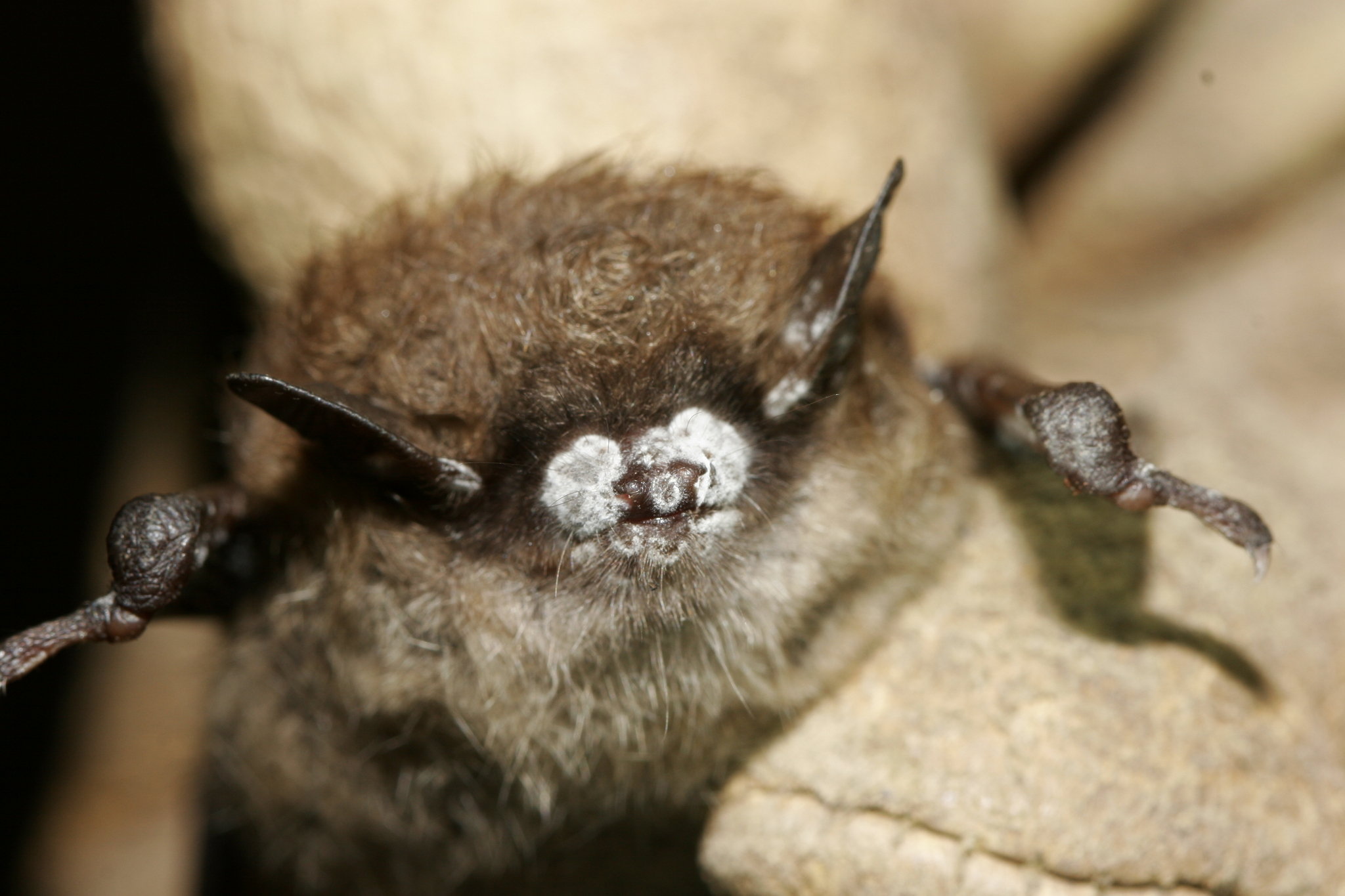

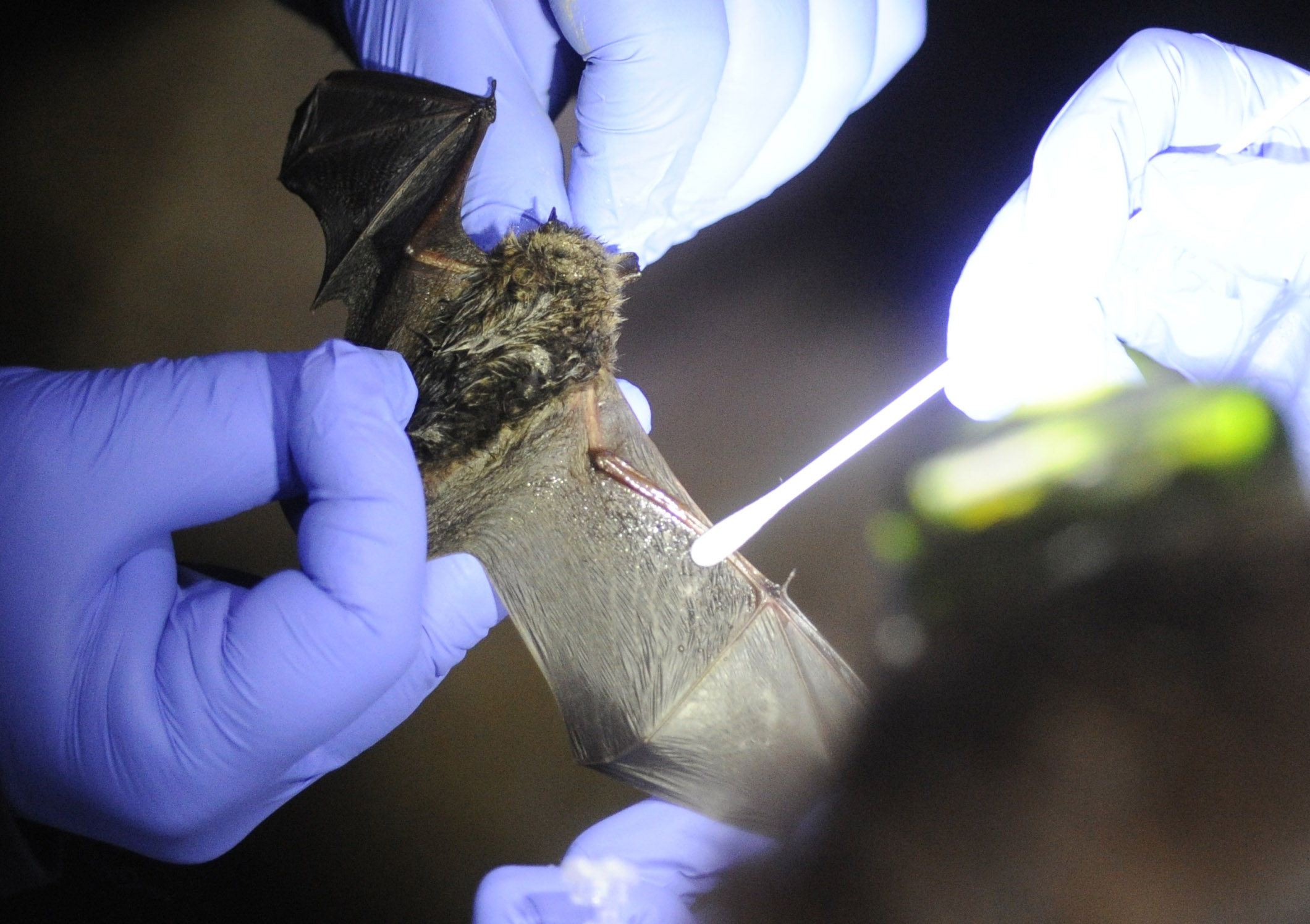
Some researchers are trying are trying to save bats by manipulating their microbiomes. Blehert says scientists have started to make progress preventing white-nose syndrome’s spread. They discovered that once the fungus enters a cave’s soil it persists for long periods of time, allowing it to travel on the shoe of a spelunker or on the wing of a bat. Scientists and recreational cavers have begun to take precautionary measures to decontaminate clothes and equipment.
Researchers are also looking into more dramatic ways to fight the disease, including innovative vaccination efforts and cutting-edge biological control methods that manipulate the microbes on a bat’s skin so its microbiome develops a resistance to the pathogen. Researchers have found that bats’ immune systems, which largely shut down during hibernation, do not notice to the invasion of Pd fungus, allowing the pathogen to easily out-compete the microbes on bats’ skin that normally fight off germs. Scientists are trying to introduce new organisms to bats’ microbiome that could resist the fungus.

The US government is starting to care about bats. The kind of research needed to counteract white-nose syndrome can be extremely complicated and often costly. Organizations like the Nature Conservancy and bat expert Merlin Tuttle’s Bat Conservation International have made funding available to study white-nose syndrome, but the disease is not going away anytime soon and there is always a worry about how sustainable such funding will be.
Luckily, the US government has also stepped in. At the end of last month, the US Fish and Wildlife Service announced that it was giving another $2.5 million in grants for white-nose syndrome research. Since 2008, the agency has donated nearly $24 million to federal, state, and nongovernmental organizations to study and prevent the disease.
Researchers like Blehert and Maine also hope the new findings showing bats’ economic value will encourage support from spheres outside of wildlife conservation. “It’s not only ethical, but there is an economic incentive [to conserve bats] too,” Maine told me. “For a lot of people, this [latter] argument is really persuasive.”
Correction: An earlier version of this article misstated that white-nose syndrome has arrived in Wyoming; it has not yet been identified there.