This story was originally published by Newsweek and is reproduced here as part of the Climate Desk collaboration.
The past four years of punishing drought have badly hurt California’s forests. Rain was scarce, the days were too hot, and this year’s wildfire season was the worst anyone has seen in years, burning up nearly 10 million acres across the West. For the first time, a team of researchers has measured the severity of the blow the drought dealt the trees, uncovering potential future destruction in the process. The resulting paper, published Monday in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, is a rich visual testament to just how much California needs its trees and how close the state is to losing 58 million of them.
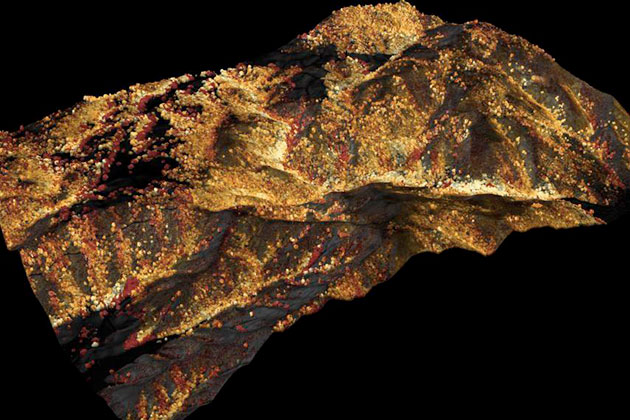
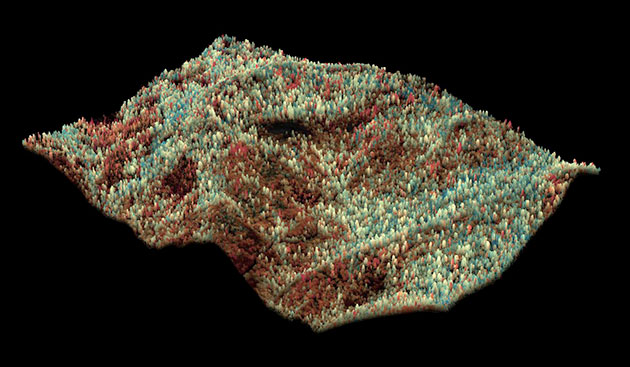
A team at the Carnegie Institution for Science, led by ecologist Greg Asner, used a laser-guided imaging tool, more properly referred to as high-fidelity imaging spectroscopy (HiFIS), mounted on a plane to sweep over California, taking snapshots that revealed how much water content the forest canopy had lost over time. In these images, the trees that appear red and orange are severely depleted of water. Light trees, in shades of tan, are trees under “drought stress” resulting from this past year’s dry season. The trees colored in blue are “doing okay,” Asner says.
In total, the team found that up to 58 million large trees, shown in red, have been heavily impacted by the drought. If the drought recurs, or if the El Niño keeps the heat turned up in the region, Asner says these trees will likely die. New tree growth would also be suppressed, leaving room for shrublands or grasslands to take over, destroying the current ecosystem of plants and animals entirely. That poses a host of new questions for wildlife management and conservation. “For example,” Asner says, “if we’re going to lose habitat, what does that mean for bear populations?”
Losing these trees also means unleashing a torrent of greenhouse gases. A significant amount of carbon is stored in tree trunks and would be released back into the atmosphere, adding to the state’s emissions, which contribute to climate change. Asner is currently working to calculate how much emissions the death of these trees could cause, but “it’s going to be substantial,” he says.
What’s more, a vital part of California’s water system would be lost. Forest soil acts as a sponge for the freshwater that melts off snowy mountains, holding the water and allowing it to “basically leak out” over time, “giving us that ability to have a more constant amount of water flowing out of the mountain system over the dry summer months,” says Asner. Forests’ ability to hold water is why, in part, they feel cool. Walking through scrubland, in contrast, is a hot experience, largely because its much drier soil does not hold water. If California loses those 58 million trees, the snowmelt and rainfall would pass through the landscapes they previously occupied without being trapped, becoming susceptible to quick evaporation, Asner explains. “We can expect that this critical water mediating service will be impacted.”
Another 888 million trees, or about 41,000 square miles of California forest, are drought-stressed. While not as urgently severe, stress is still dangerous. The dreaded bark beetle, which infests trees and almost always kills them, has been thriving in the warmer climate, Asner says, and these weakened trees are a prime target. “During drought, when trees are stressed, they’re more susceptible to infestation. The interaction between the bark beetle, the tree, and climate—we’re just figuring it out now.”
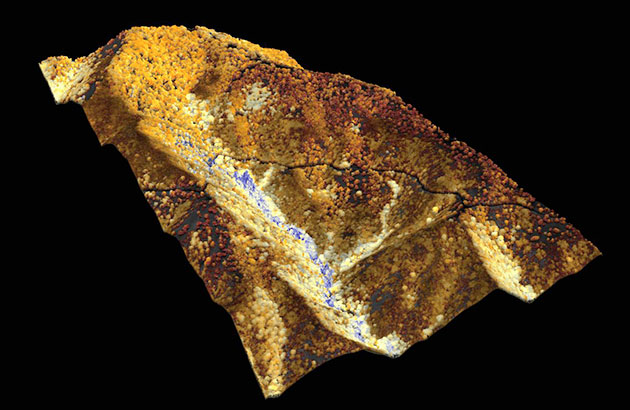
The three-dimensional renderings from the laser-mounted plane revealed a dappled landscape of tree health across the state. “The problem is geographically complex,” Asner says. “It’s not like the whole forest went down evenly in its water content.” For example, on steep terrain, where any water that might be available would quickly drain off, trees typically did worse. In valleys, where the water pools, trees are typically healthier.
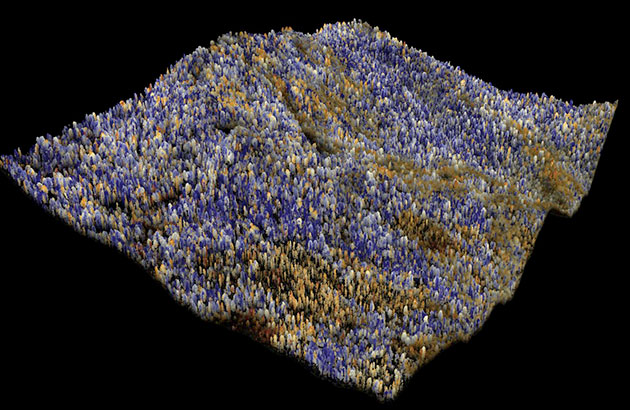
Meanwhile, places where there are stressed or severely water-depleted trees are far more likely to be the sites of future wildfires. Asner hopes these maps will help California understand the “good, the bad, and the ugly” about the state of its forests and help agencies make informed decisions about where to put resources when it comes to anticipating wildfires next season—where to thin forests in places that are most likely to become tinderboxes, for example, especially the ones that butt up against places where people live. He also hopes it will help the state better plan its prescribed burns to revitalize patches of forest that can be saved.
With so much at stake, Asner says, “it’s important that we understand what we’re losing.”












