I’m a big fan of higher capital ratios (i.e., lower leverage) as a way of making the banking system safer, so I was disturbed when Tyler Cowen pointed to a new paper suggesting that high capital ratios don’t reduce the likelihood of financial crises. Instead, a team of researchers suggests that what’s more important is the type of capital a bank has. Deposits are the most stable source of funding for any bank, and liquidity is king. Put these together, and what’s important is the loan-to-deposit ratio:
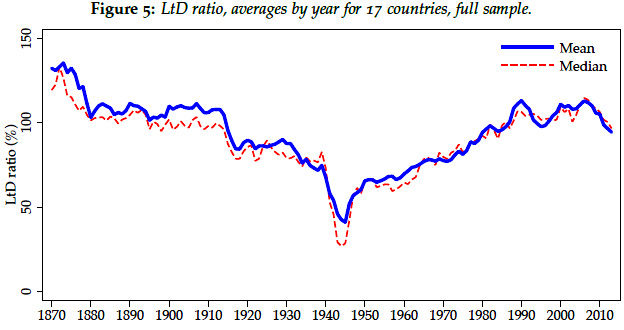
As you can see, the LtD ratio rose steadily in the postwar era, doubling from 50 percent to over 100 percent by 2008. This indicates that credit was expanding, with banks making more loans for every dollar in deposits they took in. This, the authors say, is a better predictor of financial crises than raw leverage:
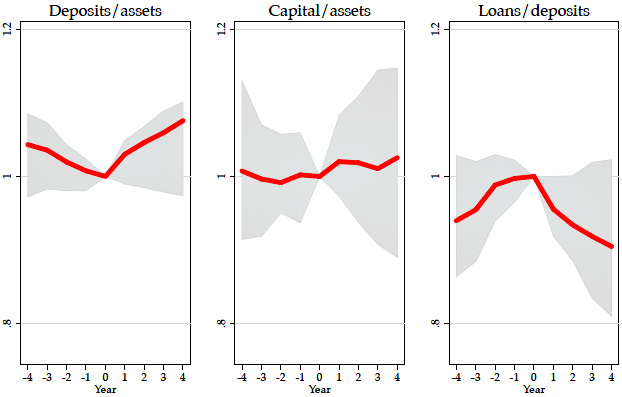
In this triptych, capital ratios are in the middle, and they don’t change much before and after a financial crisis (denoted by Year 0). However, right before a financial crisis there’s a steady decline in deposits as a percentage of total assets (which indicates a decline in the quality an;d stability of a bank’s capital base) and a steady rise in the loan-to-deposit ratio. These are the indicators that seem to be associated with financial crises.
So is there any point to higher capital standards? Yes indeed: they may not prevent financial crises, but they make recovery from a financial crisis much quicker. Just compare the green line and the red line in the charts below:
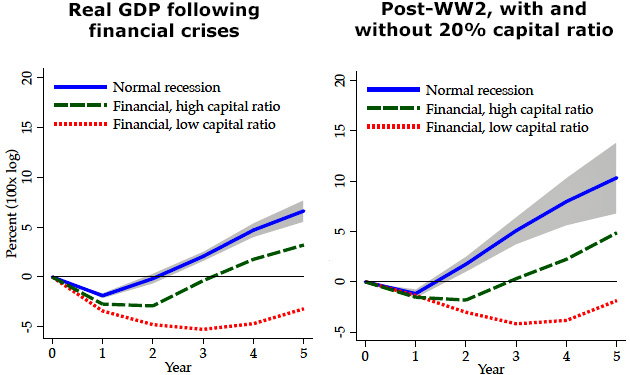
Both of these charts show the same thing: in countries with higher capital ratios, recovery from a financial crisis was far faster. Five years out, the difference was a full 13 percentage points of GDP per capita.
If these researchers are right—and I’ll add the usual caveats about this being only one study etc.—then the key to a strong, resilient banking system is twofold: a low loan-to-deposit ratio produces a liquid capital base that helps avoid financial crises, while a low leverage ratio produces the necessary capital to recover quickly if a financial crisis hits anyway.
Leverage and liquidity are key. In one sense, this is nothing new, since anyone could have told you that. But this paper suggests that they’re important for slightly different reasons than we thought.