It strikes me that it might be useful to summarize the Imperial College team’s estimate of likely coronavirus deaths. They provide mortality estimates for two scenarios: doing nothing and doing quite a large amount. What we’re doing right now is somewhere between those two, so I’ve filled it in with an interpolation. The team also provides a range of estimates for massive efforts that are strictly enforced for over a year. Here’s roughly how it pencils out:
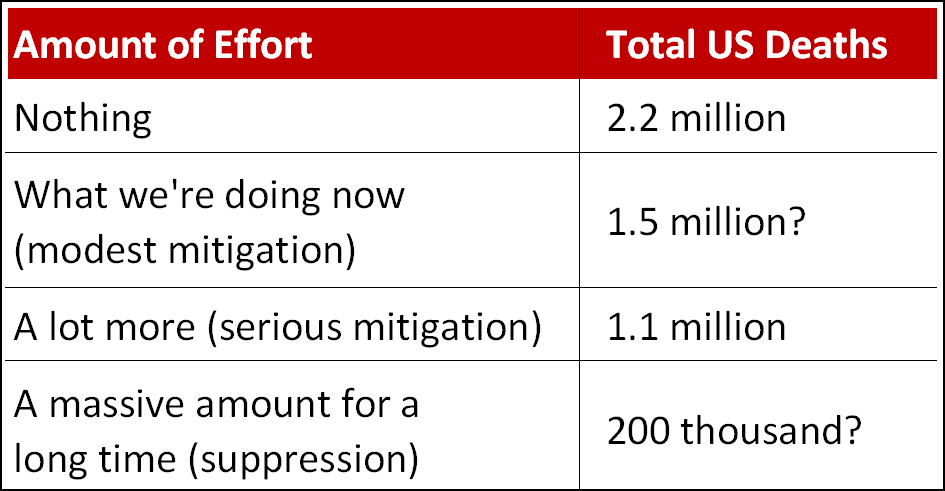
The kinds of things the IC team recommends are nowhere near being implemented yet, and to have a serious effect they need to put in place soon. Given where we are now, this means that the only realistic options are #2 and #3. In other words, it’s likely that the US will see 1.1-1.5 million deaths from the coronavirus, with more than half of them coming by June.
Now, this is just one estimate. The Imperial College team used an existing microsimulation model that was created about ten years ago and then plugged in lots of guesses and estimates: what measures would be taken; how many families would comply; average class sizes; commuting distances; incubation periods; etc. Some of these are things we have a pretty good handle on, while others are a lot trickier to estimate. Some of them produce only small changes if you get them wrong, while others are pretty sensitive. So in that sense, take this with a grain of salt.
That said, this appears to be the most sophisticated estimate we have at the moment. It might be wrong, but at this point it would be foolish to simply assume so.