Image courtesy of Wikimedia Commons
What will the Brazilian Amazon turn into once global warming makes it drier and fires become more frequent? Woods Hole Research Center and the Amazon Environmental Research Institute (IPAM) are trying to answer that question by fast forwarding to the future. How? Setting a forest on fire.
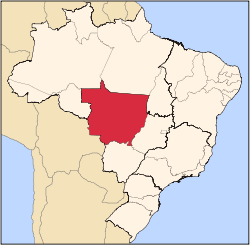
IPAM and Woods Hole have been experimenting with fire in Brazil since 2004, in a 370-acre farm in the state of Mato Grosso, Western Brazil. The area is divided in three blocks: The first is the control block, which is never burned. The second is burned every three years, and the third is burned every year. This year’s burn happened from August 28th to 31st.
They hope the burn will help determine whether this forest will survive the increasing number of wildfires—or just turn into degraded scrub or grassland. In order to figure that out, they measure forest structure, which animals and insects survive, what blossoms after a fire, and how the soil fares.
IPAM researcher Oswaldo de Carvalho Jr. says that, in the every-year burn area, degradation is already obvious. “Diversity has decreased, and other species, like common grass, start invading,” he says. Woods Hole researcher Jennifer Balch documented that trend in her field notes. “This year we were really able to capture the grass-fire cycle,” she writes. “Grass invasion via fire leads to higher fuel loads and a more intense future fire, if ignition sources are plentiful in the landscape.”
The group is also trying to answer another question: What are the carbon consequences of this high-frequency burning? So far, they have calculated that combusted organic material from the initial burn has released more than 19,000 pounds of carbon—the same as 9.5 plane trips across the US—per acre.
After a few more years of burning, Carvalho says the scientists will want to take the reverse approach. “We will study how the forest will restore itself without the fire,” he says. He believes that once they understand that, they can help the fire recovery more efficiently—an important lesson to learn to prepare for the dry years ahead.
Guest contributor Gabriela Lessa is a journalist and blogger spending the summer in her native Brazil. Watch for her regular environmental dispatches on The Blue Marble.