While there is mounting evidence for localized spillover, there have been no empirically documented cases of MPAs seeding unprotected sites, which has impeded acceptance of this management tool. Seeding is a form of population connectivity, which, in marine metapopulations, is characterized by the dispersal of planktonic larvae among local populations. Recent empirical efforts to track larval dispersal have demonstrated localized self-recruitment, but have not documented larvae seeding distant or commercially fished sites.
Determining patterns of larval dispersal is especially challenging due to the minuscule sizes of larvae and the vast ocean environment through which they travel… Therefore, we applied a new genetic parentage method to directly determine how far and to what extent the larvae of an abundant coral-reef fish disperse from their natal populations.
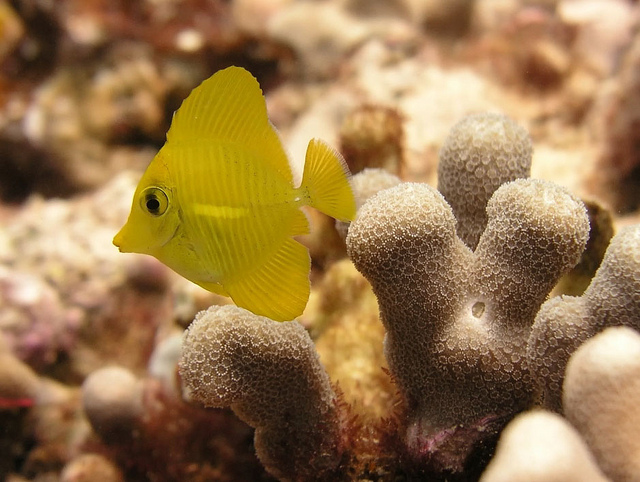
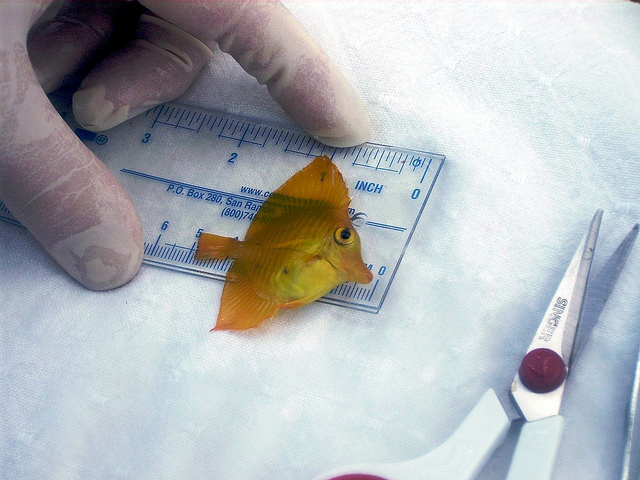
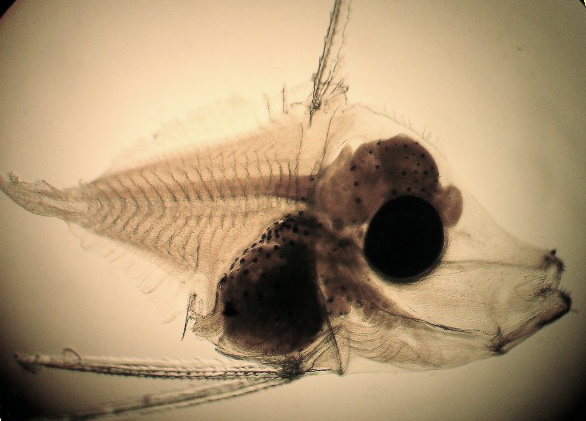 24-day-old yellow tang larva. Photo courtesy Syd Kraul.The researchers used a new Bayesian approach—a powerful statistical amplifier—to assess the genetic results on more than 1,000 adult and juvenile fish collected from nine reefs around the Big Island. Amazingly (on what must surely have been a wildly exciting day or three in the lab), they found four parent-offspring pairs:
24-day-old yellow tang larva. Photo courtesy Syd Kraul.The researchers used a new Bayesian approach—a powerful statistical amplifier—to assess the genetic results on more than 1,000 adult and juvenile fish collected from nine reefs around the Big Island. Amazingly (on what must surely have been a wildly exciting day or three in the lab), they found four parent-offspring pairs:
[W]hich is remarkable given the approximately 54-day pelagic larval duration and the large number of yellow tang around the Island of Hawai’i… All identified offspring were found between 15 and 184 kilometers to the north of their parents, suggesting that ocean currents played a substantial role in larval dispersal.
Nature’s 100-fold effect?
 Juvenile yellow tang about the size at settlement out of the pelagic zone onto the reef. Photo by Mark Hixon, courtesy Oregon State University.
Juvenile yellow tang about the size at settlement out of the pelagic zone onto the reef. Photo by Mark Hixon, courtesy Oregon State University.In addition to demonstrating the seeding effect of MPAs, documenting connectivity among marine populations has an important social and economic role. The identification of connectivity between distant reef fish populations on the Island of Hawai’i demonstrates that human coastal communities are also linked: management in one part of the ocean affects people who use another part of the ocean. Understanding connections at all levels is the foundation for truly effective ecosystem-based management.
♥ Mark R. Christie, Brian N. Tissot, Mark A. Albins, James P. Beets, Yanli Jia, Delisse M. Ortiz, Stephen E. Thompson, Mark A. Hixon. Larval Connectivity in an Effective Network of Marine Protected Areas. PLoS ONE. 5(12): e15715. DOI:10.1371/journal.pone.0015715.