Susan Chiang/iStockPhoto
It’s hard to think of another education reform idea that has garnered as much support among advocates of various ideological stripes as early childhood education. California and New York liberals support it, and so do conservatives in Oklahoma and Florida. A 2015 national poll by First Five Years Fund showed that 76 percent of voters support the idea of spending federal money to expand public preschool, and the new federal Every Student Succeeds Act includes more funding for early childhood. Helping the idea along is decades of research (which continues to pour in) that suggests effective preschools can benefit all children, especially those from disadvantaged backgrounds. “We have better evidence that preschool works and has long-term effects than we do for any other social policy,” David L. Kirp, one of our country’s leading experts on early childhood education and a professor of public policy at the University of California-Berkeley, told Mother Jones.
But can we identify what a good preschool looks like and make that accessible to the kids most in need? That topic has been debated fiercely by parents, preschool advocates, and policymakers all over the country. This week, early childhood education experts and city chiefs of preschools came together in Sacramento, California, to talk about the latest research. As presenter Abbie Lieberman, an early-education policy analyst at New America, put it: “When we step into a preschool, how can we tell what is actually learning through play and what is true chaos?”
What the Studies Say:
The growing pile of evidence on the long-term benefits of high-quality preschool stretches all the way back to a 1961 Perry Preschool Study. Researchers at the HighScope Educational Research Foundation decided to follow 123 three- and four-year-olds from public housing projects in Ypsilanti, Michigan. Fifty-eight toddlers were randomly placed in a preschool class for two years; 65 kids from the neighborhood were left without preschool. Researchers then collected data on the students until they turned 40—an astonishingly long time in education research. They found that the kids in preschool were much more likely to have better grades and test scores and more likely to go to college, earn a higher income, and own a house. In fact, their income and other assets pushed them well above the poverty line, as Kirp documents in his book, The Sandbox Investment.
A similar study started in 1972, the Abecederian Project. It followed 111 infants in North Carolina until they turned 35. The results were similar, piquing the interest of economists. Steven Barnett, a professor of economics and the executive director of the National Institute on Early Childhood Research, eventually calculated that every $1 the government invests in high-quality early education can save more than $7 later on by boosting graduation rates, reducing teen pregnancies, and even reducing crime. Such arguments about long-term savings made preschool appealing to conservatives and big philanthropists in the business world.
More recently, other scholars were able to show the disparities between students who had some form of early childhood education and those who didn’t. Jane Waldfogel, a professor of social work and public affairs at Columbia University and the author of Too Many Children Left Behind, looked at the test scores of 8,000 students in the United States and found there was a huge gap in reading abilities before kids even arrived at first grade. “If we are going to give teachers a fighting chance at narrowing our achievement gaps later in school, our kids have to come in more equally prepared,” Waldfogel told Mother Jones.
So What Does a Good Preschool Look Like?
Marjorie Wechsler, an early-childhood-education researcher at the Learning Policy Institute, recently synthesized research from a number of preschool systems and identified 10 common foundational building blocks among programs that demonstrated positive impacts on a variety of measures. Wechsler, who presented her findings in Sacramento, found that the best preschools have college-educated teachers with specialized skills in child development; they also use curriculum that emphasizes problem-solving rather than unstructured play or “repeat-after-me” drills. Successful educators know how to teach cognitive, social-emotional, and physical skills. Plus, high-quality preschools support their teachers with experienced coaches, and classroom sizes don’t get bigger than 10 kids for every teacher.
The Roadblocks:
While expanding preschool for low-income students might have garnered more advocates than almost any other school reform idea in the country, there are inevitable problems: Grover J. Whitehurst, a senior fellow at the Brookings Institution, has pointed out that studies like the Perry Preschool research have only looked at small school programs that are difficult to replicate on a large scale. Other opponents point to a recent large-scale study looking at the impact of Tennessee’s state-funded preschool; the study found that by second grade, students who attended preschool actually performed worse on tests measuring literacy, language, and math skills. The researchers, however, blamed in part repetitive, poorly structured teaching for these results.
Steven Barnett, the director of the National Institute of Early Education Research, argued in the Hechinger Report that the Tennessee study mostly provides additional evidence that preschool on the cheap doesn’t work. Perry and Abecedarian students had highly trained and well-paid teachers, and these programs cost about $14,000 to $20,000 per child in today’s dollars, compared with $4,611 that Tennessee spends currently.
And unsurprisingly, the numbers and research bolster Barnett’s point: The strongest preschools have been well funded—some estimates vary between $8,000 and $10,000 per student. Barnett pointed to New Jersey, Boston, and Tulsa, Oklahoma—places that spend energy and money on highly trained teachers, coaching, and strong curriculum—as examples of where governments are serving children well.
Is There Hope?
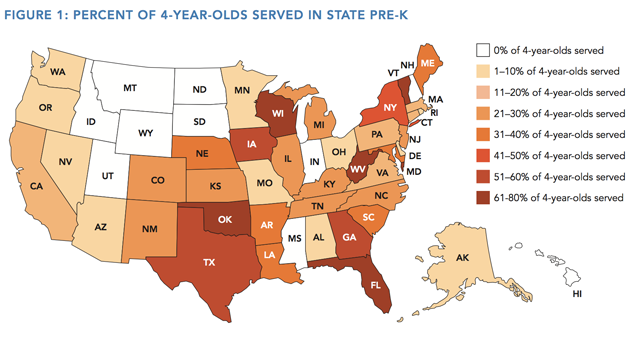
The dollar figures show the United States has a long way to go. While the city of Boston spends $10,000 for each preschooler, in 2014 the average expenditure, nationwide, was $4,125 of government spending per kid. That’s not much more than the government was spending a decade earlier.
The good news is that after years of dismal cuts following the recession, a movement to increase funding and enrollment for preschool is regaining its momentum—driven mostly by local and state policymakers. What’s more, both the federal Every Children Succeeds Act and California’s state budget include more funding to increase the number of low-income kids in high-quality preschools.
Getting the United States all the way to universal preschool, of course, is a long road. The nation ranks 30th out of 44 for preschool enrollment among developed nations; 66 percent of American four-year-olds went to preschool in 2012. Of those, only 13 percent of low-income children were enrolled in high-quality early childhood programs, according to a study by RAND Corp.
“Six years ago, we started talking about what does quality look like? How does it work?” Camille Maben, the executive director of First 5 California, a state agency, said at the end of the Sacramento gathering. “We know now that quality works in all kinds of different ways. One size truly does not fit all. But when there are so many of us, changes are like turning an elephant in the bathtub. It’s an enormous challenge.”













